Mesophotic reefs offer marine 'life boat'
 A new report offers a glimmer of hope to those managing the impact of bleaching on the Great Barrier Reef.
A new report offers a glimmer of hope to those managing the impact of bleaching on the Great Barrier Reef.
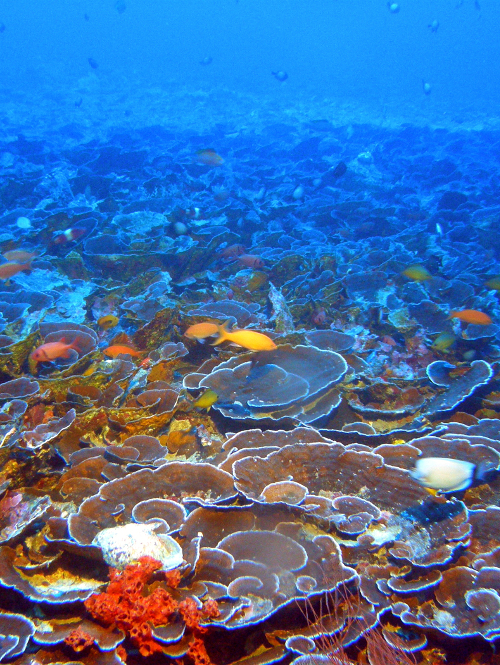
Coral bleaching has affected virtually the entire Great Barrier Reef and many other coral reef systems around the world.
It is the result of the continuing rise in global temperatures, and exacerbated by the summer’s major El Niño event.
But now, a report by 35 authors from the United Nations Environmental Programme – including Sydney University’s Professor Elaine Baker – say that as the world's surface reefs are being threatened, part of the ecosystem may survive in these barely known deeper environments, known as mesophotic coral ecosystems (MCEs).
Shallow coral reefs down to about 40 metres depth are just a hint of the ocean’s extensive coral ecosystem.
MCEs are intermediate depth reefs starting at about 40 metres depth and continuing to around 150 metres.
The report – ‘Mesophotic Coral Ecosystems A lifeboat for coral reefs?’ (PDF) – looks at the role MCEs could play in the preservation of shallower reefs.
The report asks if MCEs can provide a refuge for the species under threat in shallower reef ecosystems and whether they can provide the stock to re-populate shallow reefs if they continue to decline.
“Mesophotic coral ecosystems are a seed bank for some organisms,” said Professor Baker.
“More research needs to be done to firmly establish the role of MCEs in preserving our reefs; they aren’t a silver bullet but they may be able to resist the most immediate impacts of climate change -- thereby providing a refuge for some species and potentially helping to replenish destroyed surface reef and fish populations.
“It may be that the cooler, deeper water in MCEs could be more hospitable to many species than the warmer surface water,” she said.
“They also are less prone to waves and turbulence, therefore potentially offering a more stable environment.”
The review brought together information on the geology, biology, distribution and socio-economic aspects of mesophotic reefs in order to examine their potential resilience.
It found some deep mesophotic coral ecosystems may be less vulnerable to the most extreme ocean warming, but others may be just as vulnerable as their shallow counterparts and cannot be relied on to act as “life boats”.







 Print
Print